This article explains how to enable the CAN bus on ODROID-N2 via HW SPI interface. The detailed instructions to acquire data via a MCP2515 Bus Monitor board are documented here, as well.

H/W connection
The following products are required to configure the hardware:
- ODROID-N2
- Tinkering kit
- MCP2515 CAN module



Reference circuit
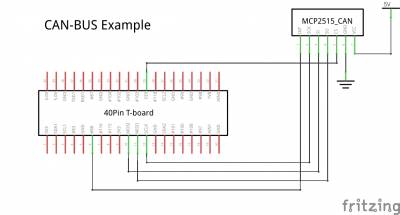
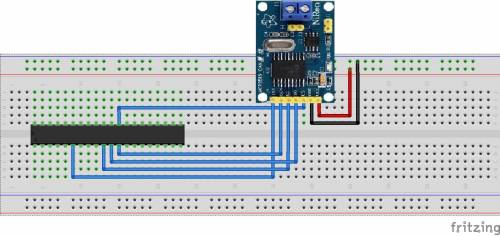
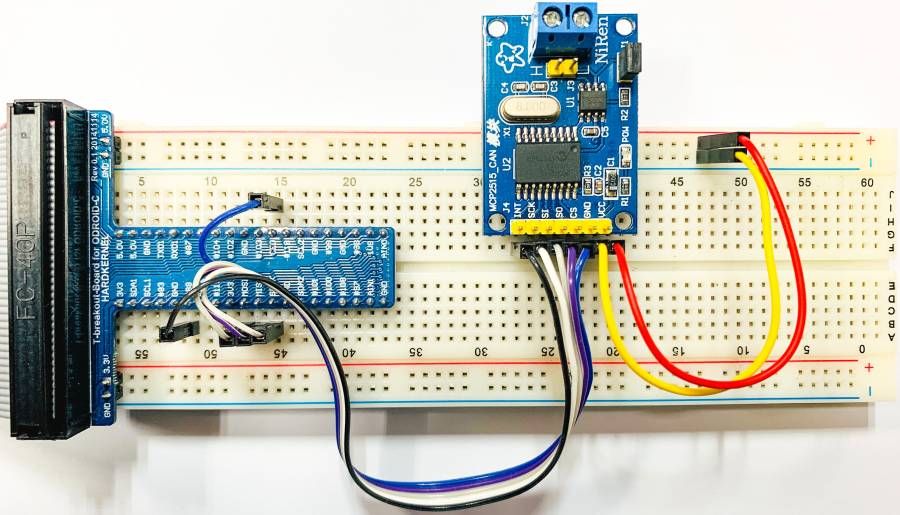
With tinkering kit
Software installation
Note:
- Operation confirmed with ODROID-N2 Ubuntu minimal image on 4.9.205-64 kernel.
- The can-bus example uses the same cs-pin as spidev, so both must not be enabled at the same time.
- If spidev is enabled, the can-bus may not work properly.
Updating of the kernel is highly recommended. This is available with Linux odroid 4.9.205-64 or higher version
root@odroid:~# apt update && apt full-upgradeEnable the modules using **device-tree-compiler**
root@odroid:~# apt install device-tree-compilerChange the status to **okay** on the SPI nodes of the device tree.
# SPICC0
root@odroid:~# fdtput -t s /media/boot/meson64_odroidn2.dtb \
/soc/cbus@ffd00000/spi@13000
[status okay
root@odroid:~#
# can0
root@odroid:~# fdtput -t s /media/boot/meson64_odroidn2.dtb \
/soc/cbus@ffd00000/spi@13000/can@0
status okay
root@odroid:~#
Check if the status changed.
# SPICC0
root@odroid:~# fdtget /media/boot/meson64_odroidn2.dtb \
/soc/cbus@ffd00000/spi@13000
Status okay
root@odroid:~#
# can0
root@odroid:~# fdtget /media/boot/meson64_odroidn2.dtb \
/soc/cbus@ffd00000/spi@13000/can@0
Status okay
root@odroid:~#
Then reboot to apply the changes. you can also check if the modules were correctly loaded.
root@odroid:~# lsmod | grep spi spi_meson_spicc 20480 0 root@odroid:~# lsmod | grep mcp251x mcp251x 24576 0 can_dev 24576 1 mcp251x root@odroid:~#
Verifying CAN support configuration
Verify the CAN host driver is registered correctly.
root@odroid:~# ls /sys/class/net/
can0 eth0 lo
root@odroid:~# ifconfig can0
can0: flags=128 mtu 16
unspec 00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00 txqueuelen 10 (UNSPEC)
RX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
root@odroid:~#
Power on the CAN hardware. Set the bitrate before performing all operations Example: Set the bitrate of the can0 interface to 125kbps:
root@odroid:~# ip link set can0 type can bitrate 125000 triple-sampling on
root@odroid:~# ifconfig can0 up
root@odroid:~# ifconfig
can0: flags=193<UP,RUNNING,NOARP> mtu 16
unspec 00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00-00 txqueuelen 10 (UNSPEC)
RX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
eth0: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet 192.168.10.8 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.10.255
inet6 fe80::e160:7710:5360:f82a prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20
ether 02:00:00:0d:1d:01 txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
RX packets 24 bytes 6066 (6.0 KB)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 54 bytes 6420 (6.4 KB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
device interrupt 22
lo: flags=73<UP,LOOPBACK,RUNNING> mtu 65536
inet 127.0.0.1 netmask 255.0.0.0
inet6 ::1 prefixlen 128 scopeid 0x10
loop txqueuelen 1 (Local Loopback)
RX packets 129 bytes 10117 (10.1 KB)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 129 bytes 10117 (10.1 KB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
root@odroid:~#
Install the SocketCAN utils.
The can-utils package is a collection of CAN drivers and networking tools for Linux. It allows interfacing with CAN bus devices in a similar fashion as other network devices.
sudo apt install can-utilsWe need to perform the Loopback test on a single CAN port. Set loopback mode on can0
ifconfig can0 down
ip link set can0 type can bitrate 125000 loopback on
ifconfig can0 up
ip -details link show can0
root@odroid:~# ifconfig can0 down
root@odroid:~# ip link set can0 type can bitrate 125000 loopback on
root@odroid:~# ifconfig can0 up
root@odroid:~# ip -details link show can0
3: can0: <NOARP,UP,LOWER_UP,ECHO> mtu 16 qdisc fq_codel state UNKNOWN mode DEFAULT group default qlen 10
link/can promiscuity 0
can <LOOPBACK,TRIPLE-SAMPLING> state ERROR-ACTIVE restart-ms 0
bitrate 125000 sample-point 0.850
tq 400 prop-seg 8 phase-seg1 8 phase-seg2 3 sjw 1
mcp251x: tseg1 3..16 tseg2 2..8 sjw 1..4 brp 1..64 brp-inc 1
clock 5000000numtxqueues 1 numrxqueues 1 gso_max_size 65536 gso_max_segs 65535
root@odroid:~#
The following command shows the received message from the CAN bus
candump can0On a second terminal, The following command sends 3 bytes on the bus (0x11, 0x22, 0x33) with the identifier 500.
cansend can0 500#11.22.33
How to test CAN-bus link between 2 ODROID-N2 boards
Connect CANL, CANH pins between two ODROID-N2 boards
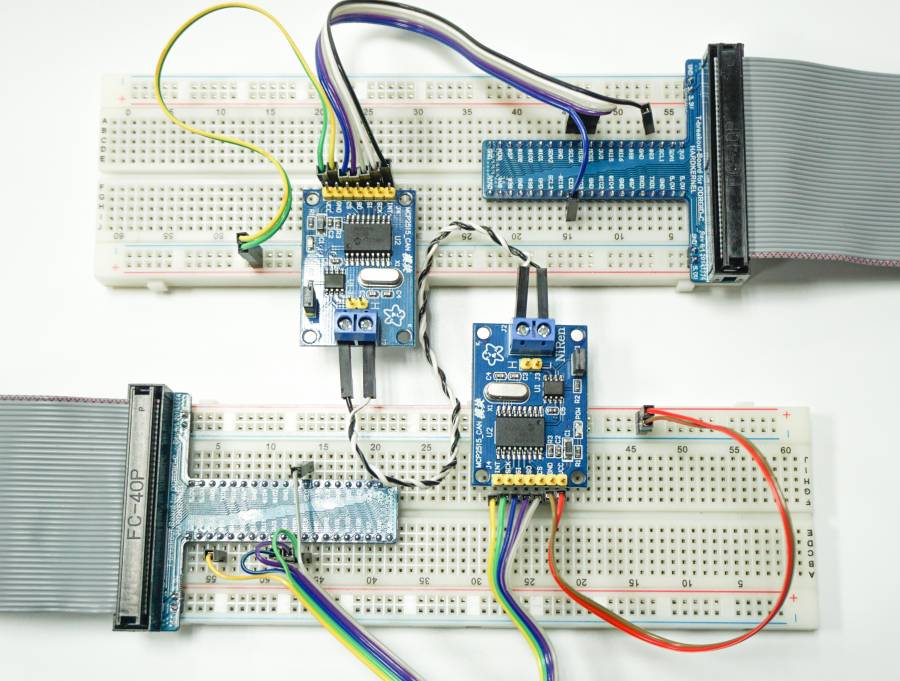
Power-up both boards and type the following into the shell of both boards for configuring the CAN bus device:
ip link set can0 type can bitrate 125000 triple-sampling on ifconfig can0 upType the following into the shell of board 1 (which is used for testing/receiving over the can0 device):
candump can0Type the following into the shell of board 2 (which is used for testing/sending data packets over the can0 device):
cansend can0 500#11.22.33At this point, board 1 will receive the data packet sent from board 2:
root@odroid:~# candump can0 can0 500 [3] 11 22 33 can0 500 [3] 11 22 33
References
https://wiki.odroid.com/odroid-n2/application_note/gpio/can-bus

Be the first to comment