
Composite video is an analog video transmission that was popular before the age of digital television, with supported resolutions of 480i and 576i. The ODROID-N2 supports this video feature, and is designed to connect with a TV through its audio jack.
Hardware connection
The Composite Video Blanking and Sync (CVBS) video signal is assigned to the audio connector (CON6) and TV can be connected with a specialized cable available from Hardkernel at https://www.hardkernel.com/shop/3-5mm-male-plug-to-3-rca-female-audio-video-cable/.
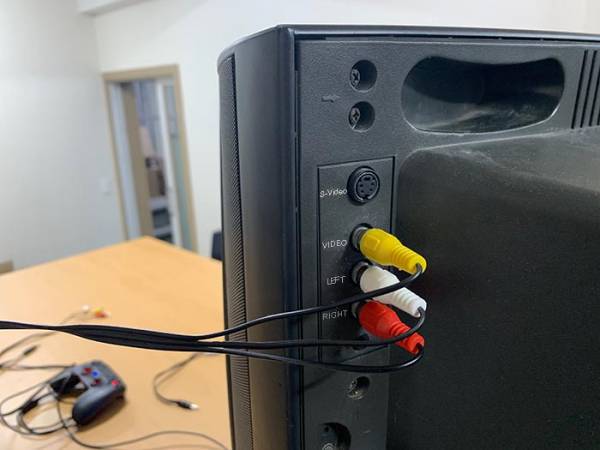

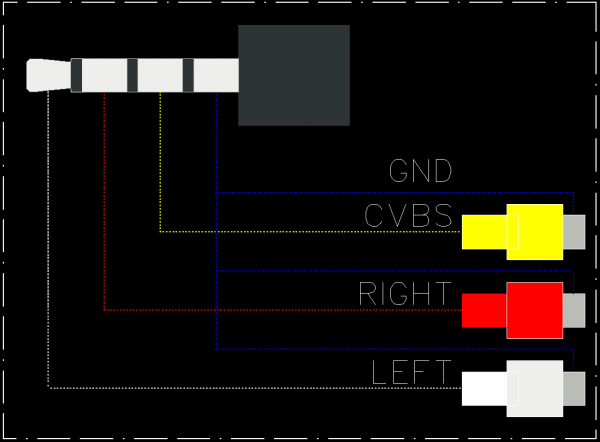

Software configuration
In order to select CVBS as a display output rather than HDMI, the Linux kernel command line must be configured properly and HDMI cable must not be attached. The CVBS picture format can be set in the boot.ini file:
# NTSC
setenv cvbsmode "480cvbs"
# PAL
#setenv cvbsmode "576cvbs"
setenv bootargs "${bootargs} cvbsmode=${cvbsmode} cvbscable=${cvbscable}"
For example, if the TV supports 480CVBS picture format and its cable is connected, the Linux kernel command line would look like this:
$ cat /proc/cmdline
console=ttyS0,115200n8 ... cvbsmode=480cvbs cvbscable=1 ...
Overscan (Android)
The Android operating system supports a zoom in/out method in order to manage the overscan. You can adjust it via the ODROID Settings Android app, or by directly editing the boot.ini file. The zoom rate value is between from 80% and 100%:
# Display Zoom Rate
setenv zoom_rate "100"
# Shrink the picture as 10%
setenv overscan=10
setenv bootargs "${bootargs} overscan=${overscan}"
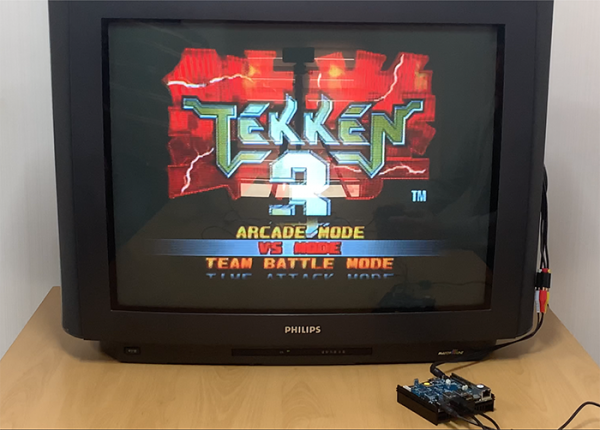
For comments, questions, and suggestions, please visit the original Wiki article at https://wiki.odroid.com/odroid-n2/application_note/cvbs. To see the ODROID-N2 using a composite video connection in action, please check out https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Uk8T1s6ufnM.

Be the first to comment